Container as a Service
Run and scale containerized workloads without managing Kubernetes clusters or virtual machines.
Overview
Container as a Service (CaaS) handles infrastructure so you can focus on your application:
- Scheduling and lifecycle management
- Scaling and auto-healing
- Load balancing and networking
- Monitoring, logging, and cost optimization
- CI/CD integration with GitHub Actions
Prerequisites
- Project dashboard or API access
- Container image (public or private registry)
- (Optional) Registry credentials for private images
- (Optional) Domain or subdomain for public endpoints
- (Optional) GitHub repository for automated deployments
Step 1: Create Container Instance
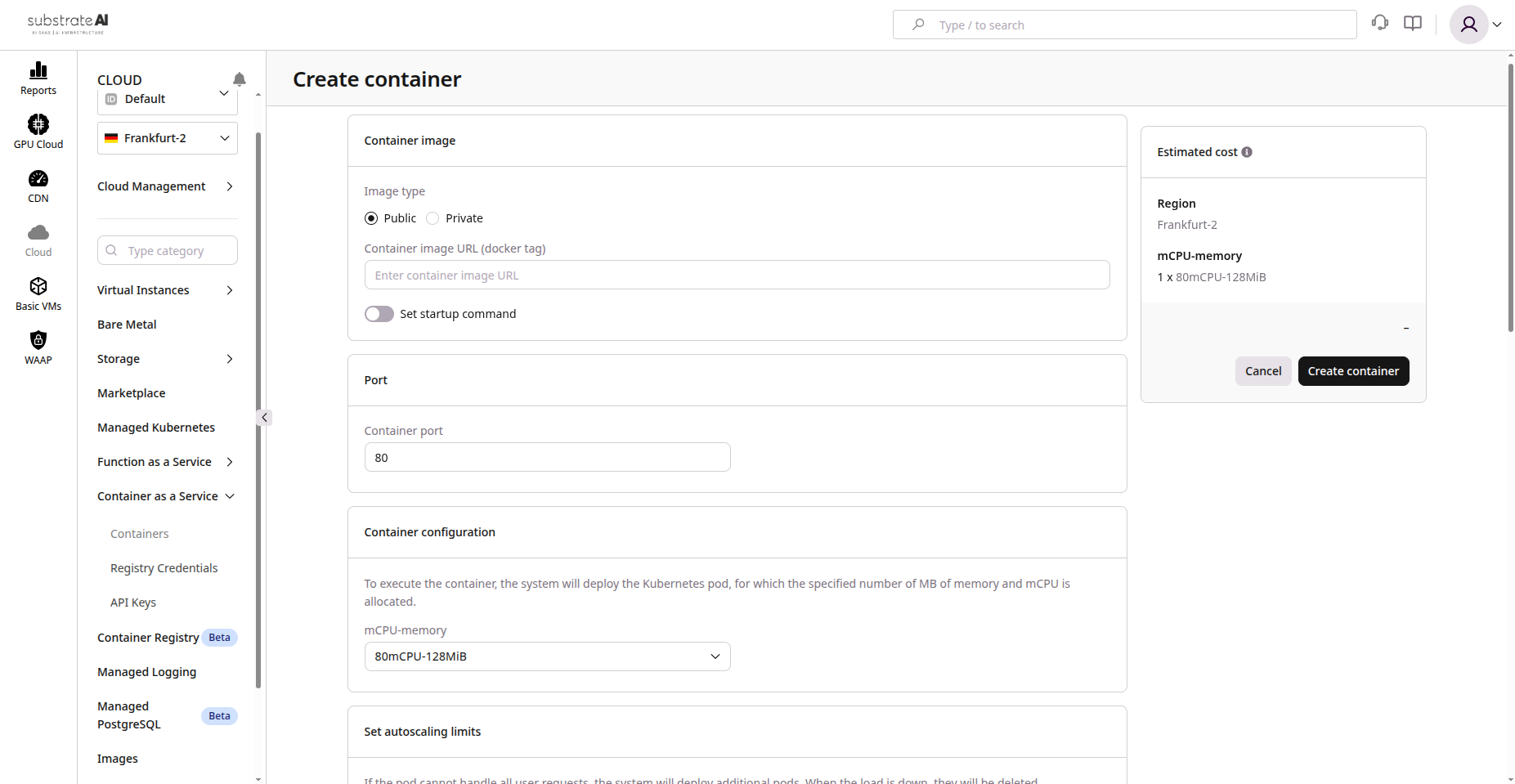
- Navigate to Compute > Container as a Service
- Click Create Container
- Configure:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Container Image | e.g., registry.example.com/app:latest |
| Registry Credentials | Required for private registries |
| Startup Command | Optional entrypoint override |
| Region/Zone | Deployment location |
| CPU and Memory | Resource allocation |
| Autoscaling | Min/max instances (e.g., 1-5) |
- Click Create
Deployment takes a few minutes. Status becomes Active when ready.
Step 2: Configure Runtime
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Ports and Protocols | HTTP, HTTPS, TCP exposure |
| Environment Variables | Credentials, API keys, configs |
| Scaling Rules | CPU, memory, or request rate thresholds |
| Container Lifetime | Scale-to-zero when idle |
| Secrets Management | Secure environment bindings |
Step 3: Networking and Access
- Each container gets a unique endpoint (public or private)
- Map custom domain via CNAME record
- Configure TLS certificates (upload or auto-generate)
- Restrict to private subnets for internal systems
Step 4: CI/CD with GitHub Actions
Example Workflow
name: Deploy Container
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Build Docker image
run: docker build -t registry.example.com/myapp:${{ github.sha }} .
- name: Log in to registry
run: echo ${{ secrets.REGISTRY_PASSWORD }} | docker login registry.example.com -u ${{ secrets.REGISTRY_USER }} --password-stdin
- name: Push image
run: docker push registry.example.com/myapp:${{ github.sha }}
- name: Deploy to CaaS
run: |
curl -X POST https://api.yourplatform.net/v1/containers/deploy \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${{ secrets.CAAS_API_KEY }}" \
-d '{"image": "registry.example.com/myapp:'${{ github.sha }}'"}'
Extend with automated tests, Slack notifications, or blue-green releases.
Step 5: Monitoring and Logs
- Monitor status, CPU/memory usage, instance count via dashboard
- Stream logs via console or API:
caas logs <container-id>
- Integrate with ELK, Loki, or CloudWatch
- Set up alerts for latency or failed deploys
Step 6: Lifecycle Management
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Start/Stop/Restart | Control containers anytime |
| Redeploy | Update with new image tag |
| Delete | Free resources from old instances |
| Rollback | Revert to previous stable image |
Features Summary
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Managed Runtime | No server or cluster management |
| Registry Support | Public and private registries |
| Autoscaling | Demand-based scaling |
| Scale-to-Zero | Suspend idle containers |
| Custom Domains | Branded URL endpoints |
| CI/CD Integration | GitHub Actions automation |
| Secrets Management | Secure config injection |
| Monitoring and Logging | Centralized metrics and logs |
| Pay-as-you-go | Charged only while running |
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Container stuck in Pending | Quota exceeded or image pull issue | Check capacity and registry credentials |
| GitHub Actions deploy failed | Invalid API token | Verify CAAS_API_KEY secret |
| Logs not visible | Logging disabled | Enable log streaming |
| Domain not resolving | Incorrect DNS | Verify CNAME and propagation |
| Autoscaling not triggering | Thresholds too high | Lower triggers, verify monitoring |